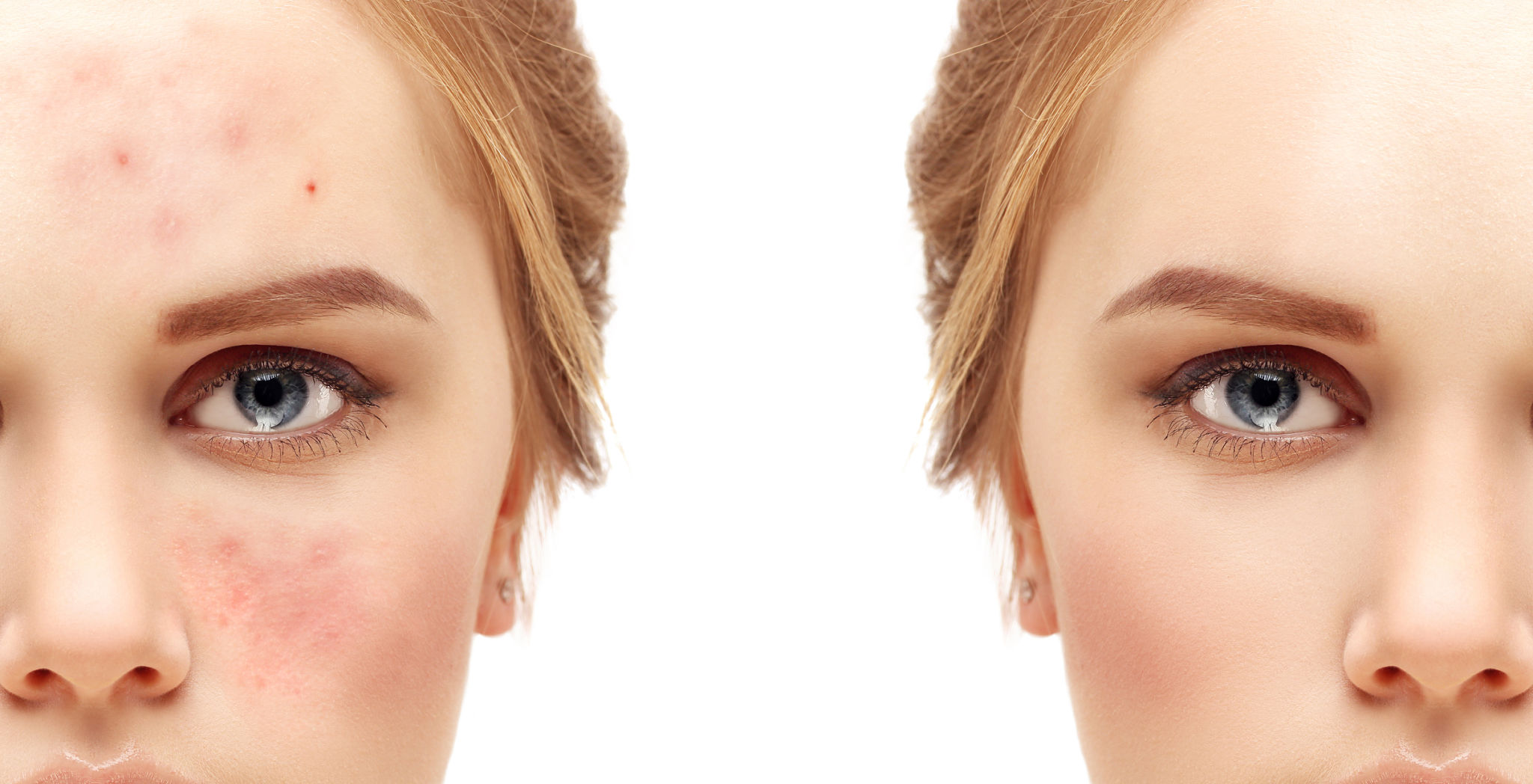
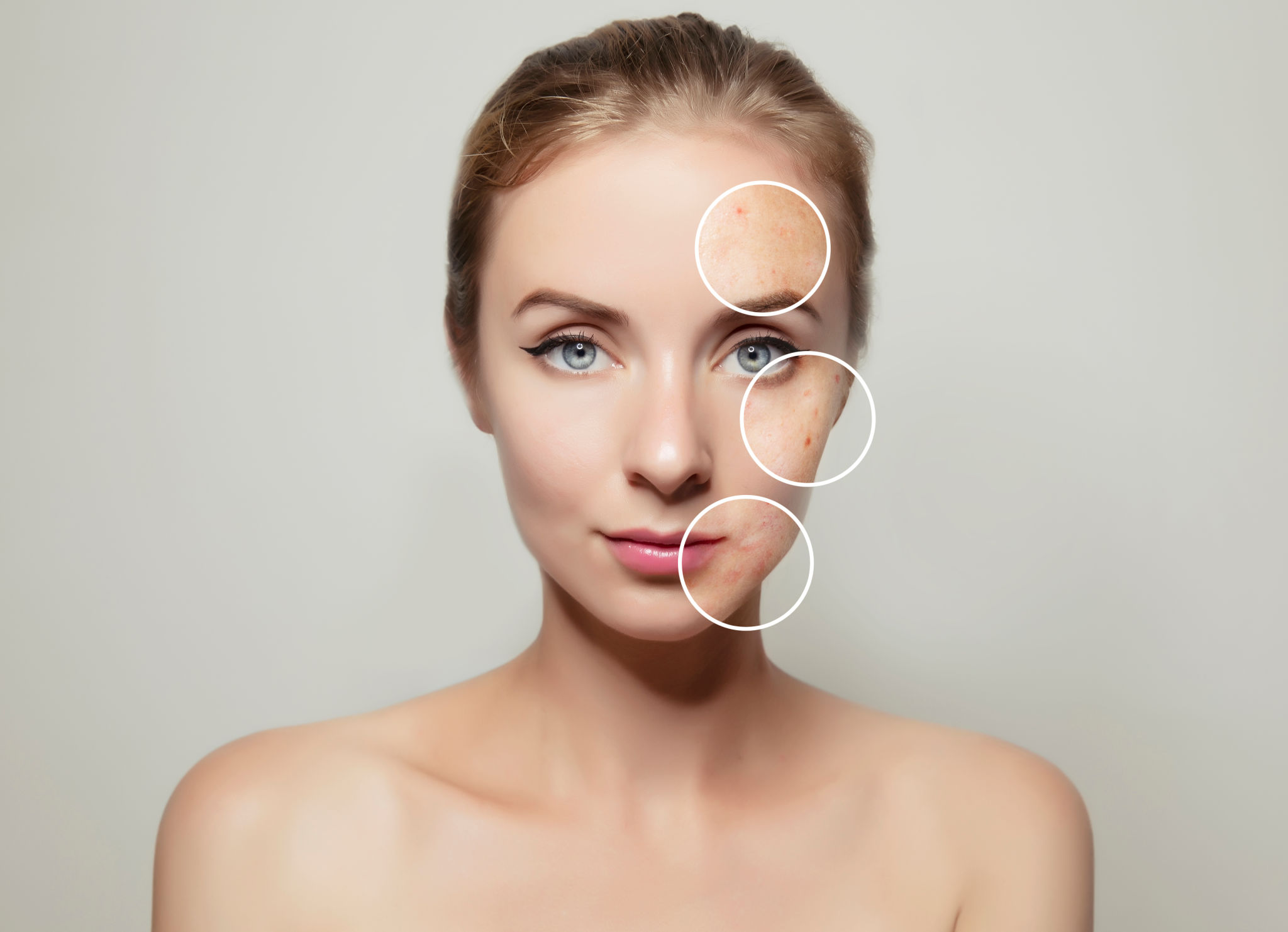
What is Acne
Types of Acne
The mixture of oil and cells allows the bacteria to grow in the plugged follicles. When this happens, a hard plug called a comedo can form. A comedo is an enlarged hair follicle. It can take the following forms:
- a blackhead, which is a comedo that reaches the skin’s surface and looks black
- a whitehead, which is a comedo that is sealed by keratin, the fibrous protein produced by the skin cells and looks like a white bump.
In addition, pimples can form on the skin. Types of pimples include:
- papules, which are small, red bumps that may be tender to the touch
- pustules, which are pus-filled lesions that are often red at the base
- nodules, which are large, painful lesions deep in the skin
- cysts, which are painful pus-filled lesions deep in the skin that can cause scarring
Acne is skin condition characterized by red pimples on the skin, especially on the face, chest and back, due to inflamed or infected sebaceous glands and prevalent chiefly among adolescents. If hair follicles become blocked by sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria, acne is the result. The sebaceous gland units are most commonly found on the face, neck, and back. During puberty, there are increased levels of the male hormone androgen. High levels of androgen cause excess sebum to form. Acne is not dangerous, but can leave skin scars.
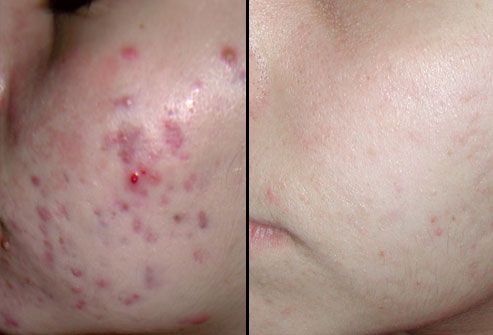
Acne is common and is usually treatable. You may need treatment for several months to clear spots. Inflamed acne needs to be treated early to prevent scarring. Once the spots are gone, you may need maintenance treatment for several years to keep the spots away.
What are the Causes and Symptoms
There are several risk factors that make acne more likely to occur:
- Age. Adolescents are more likely to have acne.
- Disease. Certain hormonal disorders such as polycystic ovarian syndrome make acne more likely.
- Hormonal changes. Acne can flare up before menstruation. An increase in the male hormone androgen during puberty (seen in both males and females) causes the sebaceous glands to overproduce androgen. Boys have more severe acne than girls.
- Heredity. Some individual are genetically more susceptible to acne.
- Drugs. Steroids and performance enhancing drugs, oral contraceptives, antibiotics, antidepressants, and tranquillizers such as lithium are known to cause acne.
- Cosmetics. Oily cosmetics can plug up hair follicles.
Other factors can worsen acne or cause it to flare up:
- Environmental irritants. Air pollution and high humidity can worsen acne, as can exposure to greasy environments such as working in a fast food restaurant.
- Friction. Rubbing the skin vigorously or exposure to constant friction from backpacks or tight collars can worsen acne.
- Personal hygiene. Picking at pimples or scrubbing the skin too hard can result in worsened acne.
Acne Treatment Procedures
Acne treatment consists of reducing the sebum production, removing dead skin cells, and killing bacteria with oral medication and drugs used on the skin (topical). The treatment depends on the severity of the condition.
How to Prevent Acne
There are no sure ways to prevent acne, but the following steps may be taken to minimize flare-ups:
- Gentle washing of affected areas once or twice every day
- Avoiding abrasive cleansers
- Using non-comedogenic (does not clog pores) makeup and moisturizers
- Shampooing often and wearing hair off the face
- Eating a well-balanced diet, avoiding foods that trigger flare-ups
- Unless told otherwise by the healthcare provider, giving dry pimples a limited amount of sun exposure
- Not picking or squeezing blemishes


