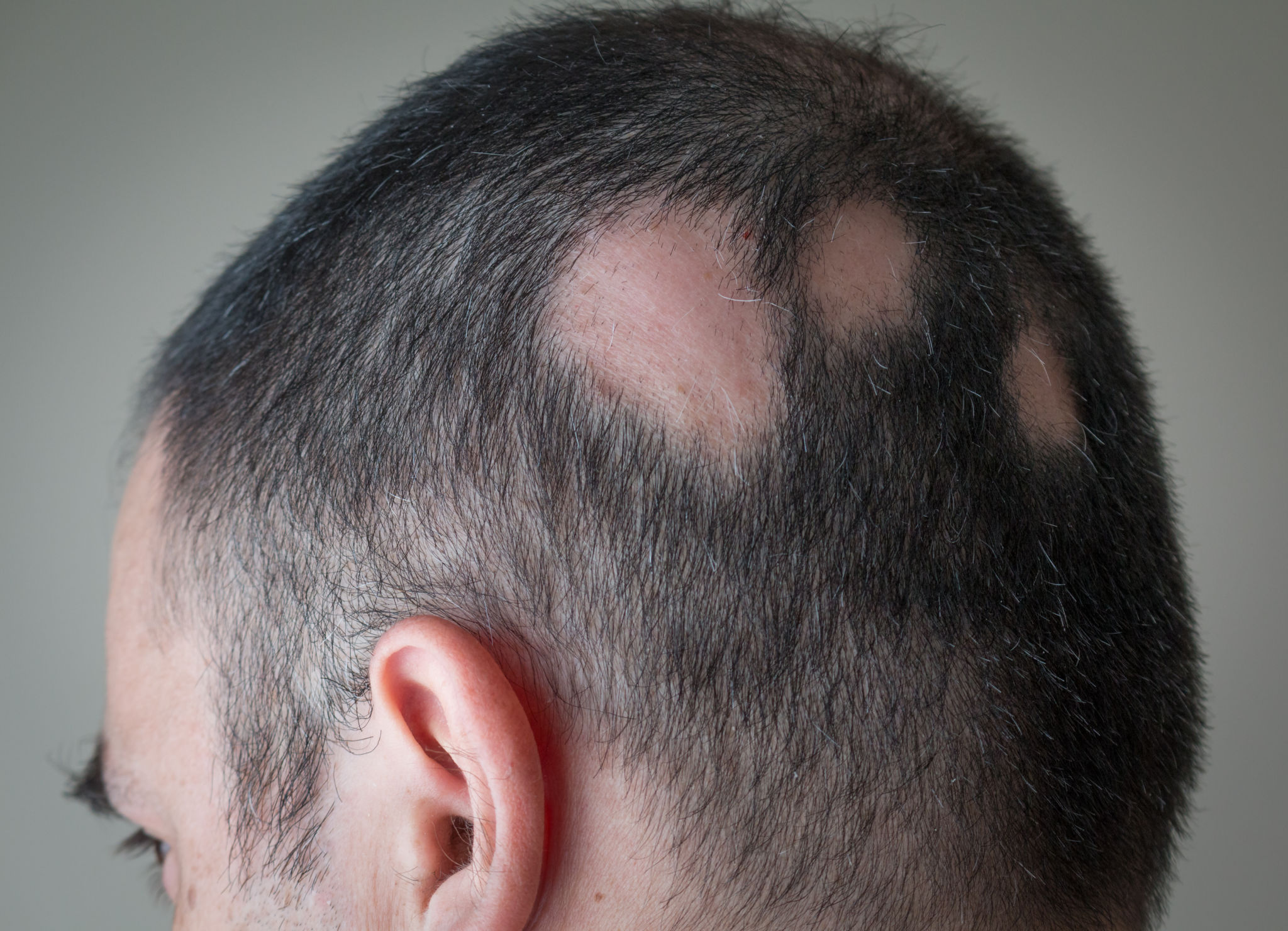
What is Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a sudden loss of hair in patches from any part of the body which, in the majority of cases, is followed by its spontaneous regrowth. It is almost always caused by psychological factors. The damage to the follicle is usually not permanent.

What are the causes for Alopecia areata
- Drug induced
- Sudden Shock or Trauma
- Local skin Disorder
- Viral infection or illness
- Pregnancy/ Hormones
- Allergic Reaction
- Genetics
Treatment
-
There is no cure for alopecia areata. Hair often re-grows on its own. Treatment can help the hair re-grow more quickly. A dermatologist may prescribe one or more of the following to help the hair re-grow more quickly:
- Corticosteroids: This medicine suppresses the immune system. It can be given as shots, with the dermatologist injecting the medicine into the places with hair loss. Sometimes a patient gets a topical (applied to the skin) form of this medicine. It may be a cream, lotion, or ointment. The patient applies the medicine to the bare spots. Less often, patients take corticosteroid pills.For adults with alopecia areata, these shots are often the first treatment tried. Patients receive shots every 3 to 6 weeks. Hair growth begins about 4 weeks after the last shot. Sometimes, it takes longer.Topical corticosteroids are less effective than shots. This is often the best treatment for children.
Corticosteroid pills can have serious side effects. Dermatologists do not routinely prescribe them for this reason. Pills may be a treatment choice for patients with many bald spots.
- Minoxidil: A hair re-growth medicine, minoxidil 5%, may help some patients re-grow their hair. Both children and adults can use it. Patients apply it twice a day to the scalp, brows, or beard. New hair may start to grow in about 3 months. Patients most often use this medicine with another treatment.
- Anthralin: This medicine alters the skin’s immune function. The patient applies a tar-like substance to the skin and leaves it on for 20 to 60 minutes. A dermatologist may call this short-contact therapy. After 20 to 60 minutes, the anthralin is washed off to avoid the skin from becoming irritated.
- Corticosteroids: This medicine suppresses the immune system. It can be given as shots, with the dermatologist injecting the medicine into the places with hair loss. Sometimes a patient gets a topical (applied to the skin) form of this medicine. It may be a cream, lotion, or ointment. The patient applies the medicine to the bare spots. Less often, patients take corticosteroid pills.For adults with alopecia areata, these shots are often the first treatment tried. Patients receive shots every 3 to 6 weeks. Hair growth begins about 4 weeks after the last shot. Sometimes, it takes longer.Topical corticosteroids are less effective than shots. This is often the best treatment for children.
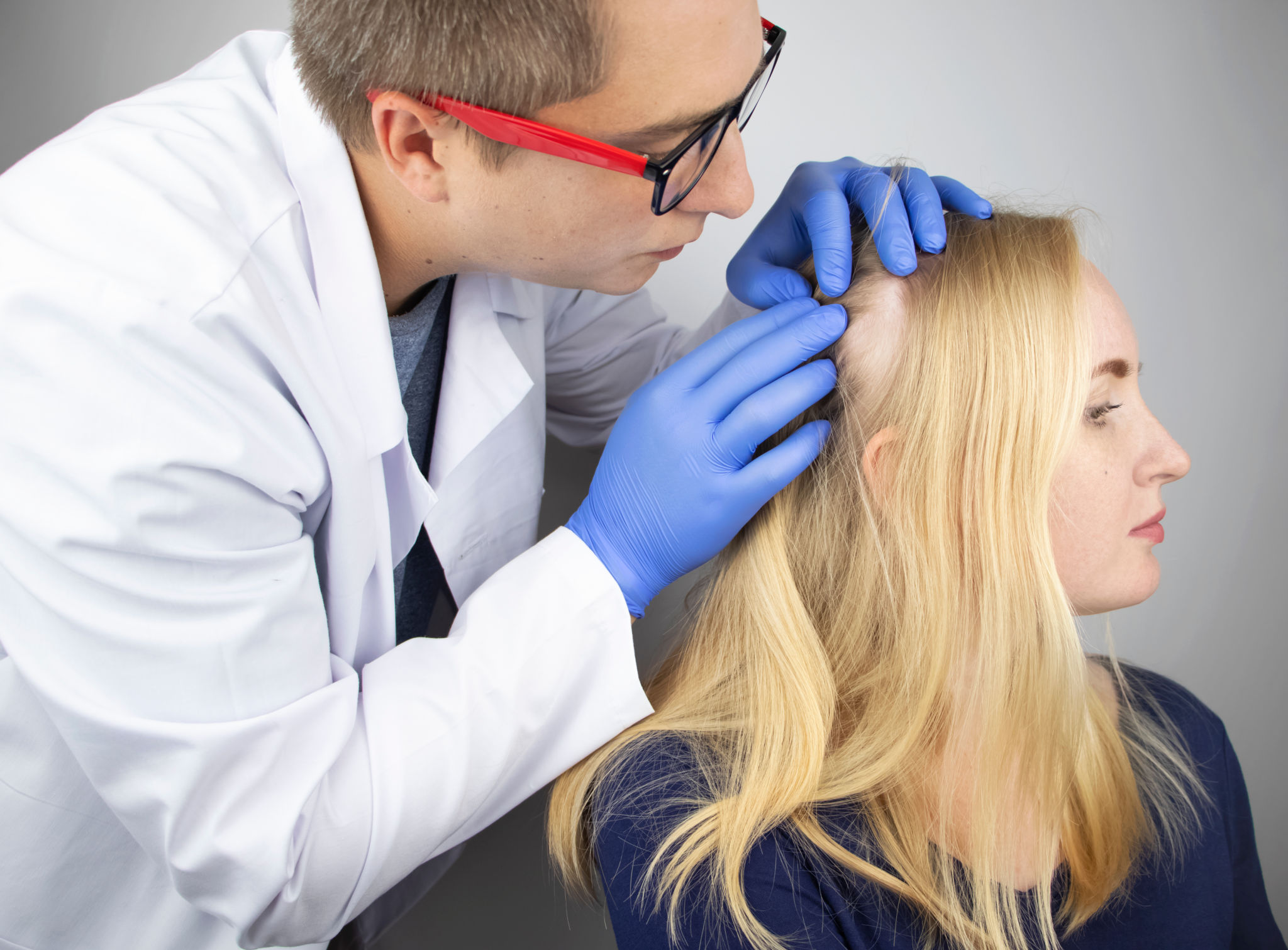
- Diphencyprone (DPCP): This medicine is applied to the bald skin. It causes a small allergic reaction. When the reaction occurs, a patient has redness, swelling, and itching. Dermatologists believe this allergic reaction tricks the immune system, causing it to send white blood cells to the surface of the scalp. This fights the inflammation. It also prevents the hair follicles from going to sleep, and causing the hair loss.With DPCP, it can take 3 months for the hair to start re-growing.
- Other treatments: Patients often get more than 1 treatment at a time. A mix of 2 or more treatments often boosts success.
