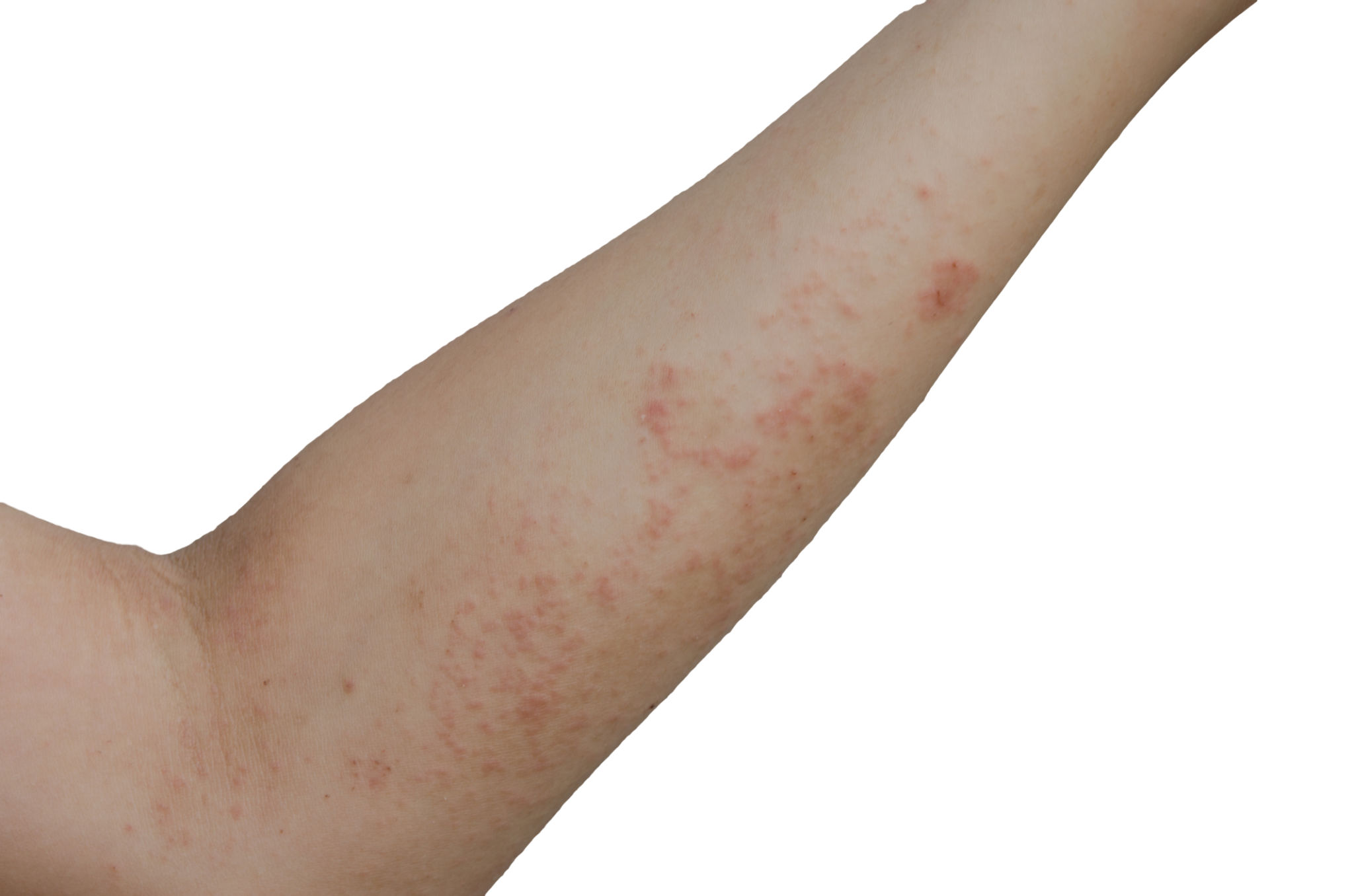
What is Scabies
Scabies is an extremely itchy skin disorder that can be passed from one person to another. Scabies is spread to others through close skin-to-skin contact. Scabies is caused by a mite (like a tiny insect) called Sarcoptes scabiei. The mite is a parasite, meaning it lives off the host (a human) with no benefit to the host.
What are Sign and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of scabies include:
-
-
- Itching, mainly at night: Itching is the most common symptom. The itch can be so intense that it keeps a person awake at night.
- Rash: Many people get the scabies rash. This rash causes little bumps that often form a line. The bumps can look like hives, tiny bites, knots under the skin, or pimples. Some people develop scaly patches that look like eczema.
- Sores: Scratching the itchy rash can cause sores. An infection can develop in the sores.
- Thick crusts on the skin: Crusts form when a person develops a severe type of scabies called crusted scabies. Another name for crusted scabies is Norwegian scabies. These crusts house 100s to 1,000s of mites and the mites’ eggs. With so many mites burrowing in the skin, the rash and itch become severe.
-
The severe itch can lead to constant scratching. With non-stop scratching, an infection can develop. Non-stop scratching can even lead to sepsis, a sometimes life-threatening condition that develops when the infection enters the blood.
- Swollen and stiff joints
Treatment
Scabies treatment includes administration of a scabicidal agent (eg, permethrin, lindane, or ivermectin), as well as an appropriate antimicrobial agent if a secondary infection has developed.