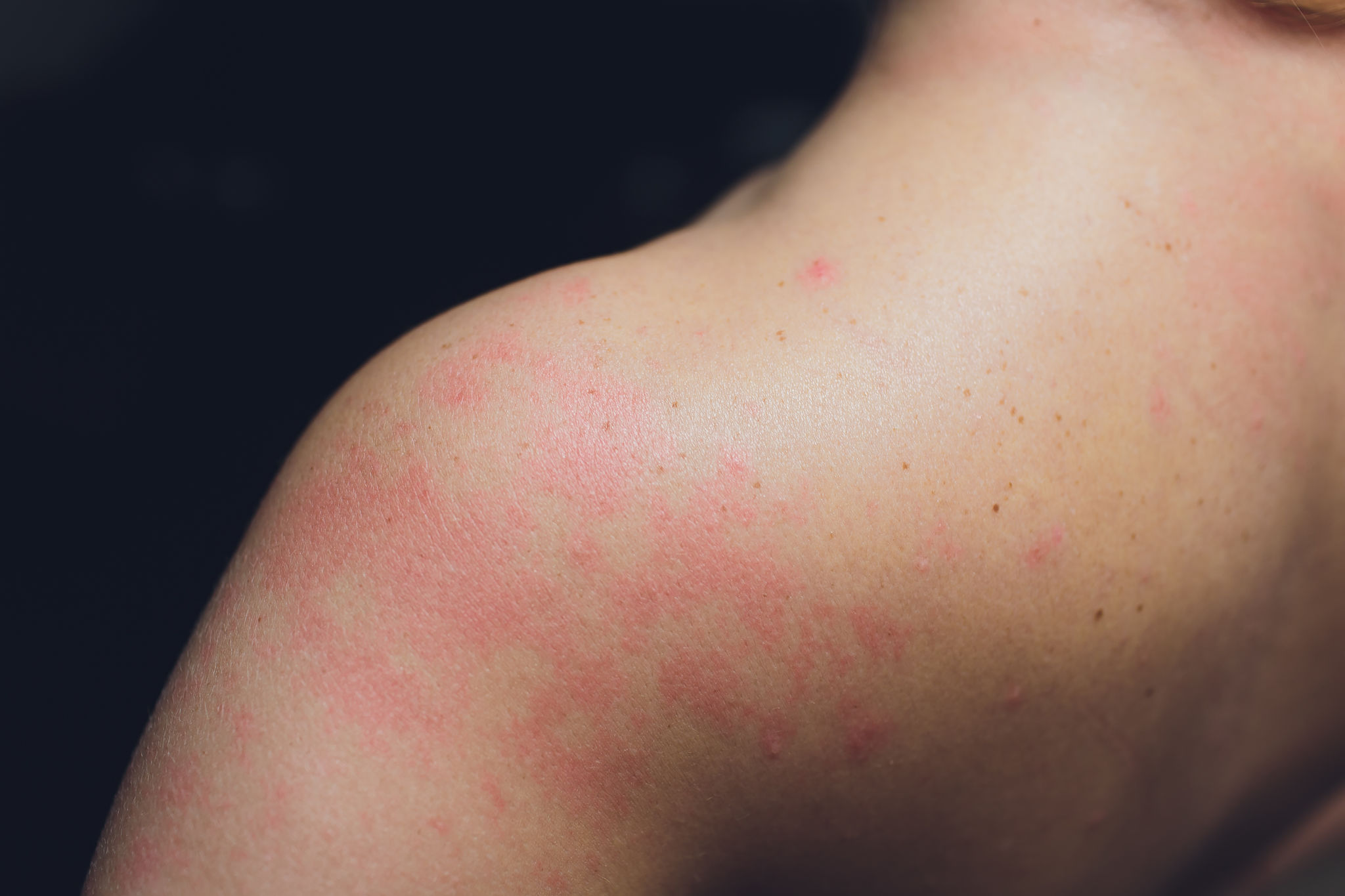
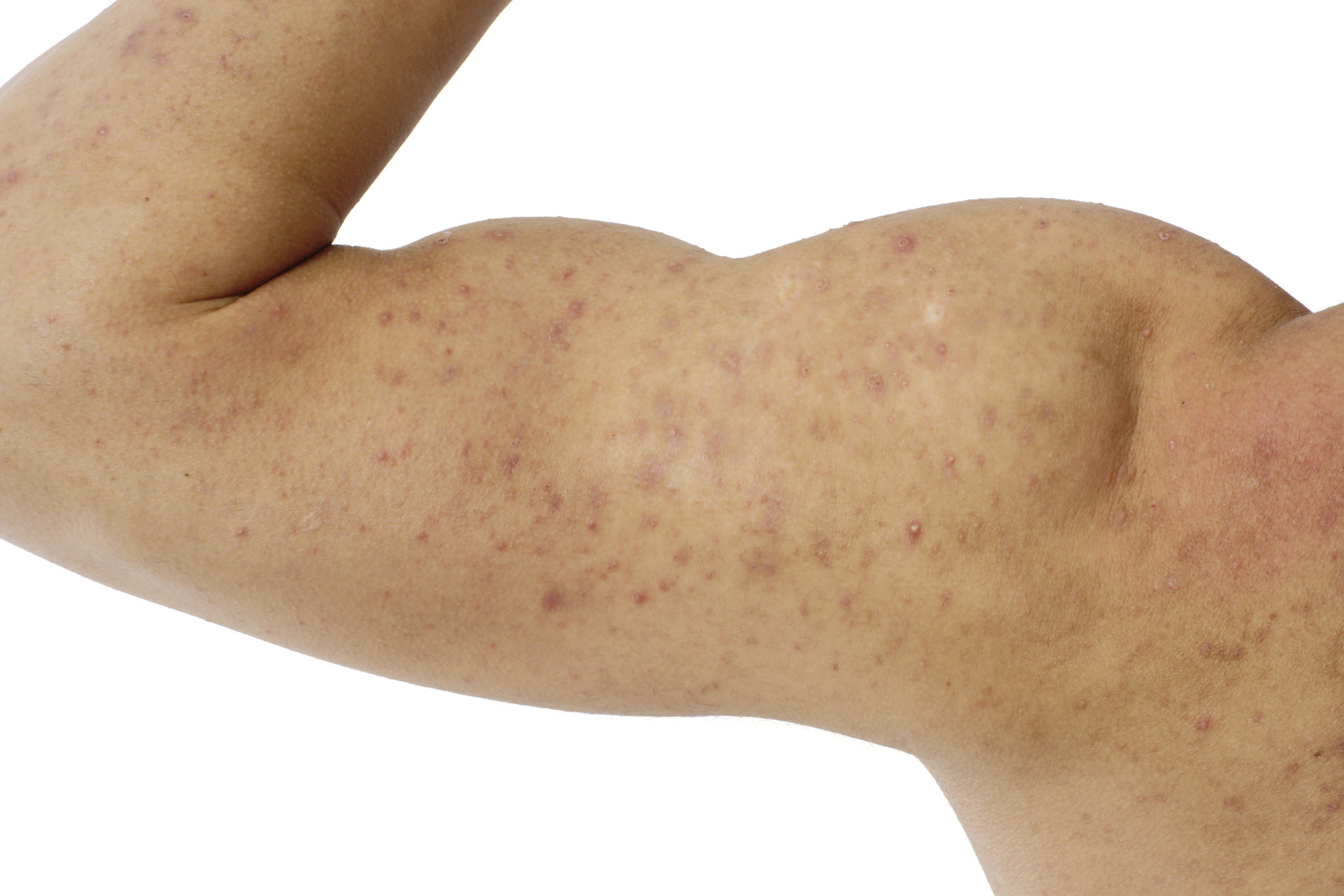
What is Urticaria
Urticaria commonly referred to as hives, is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives typically last less than 4 hours but an individual lesion may last for up to 24 hours and the whole process may stay for days or weeks.
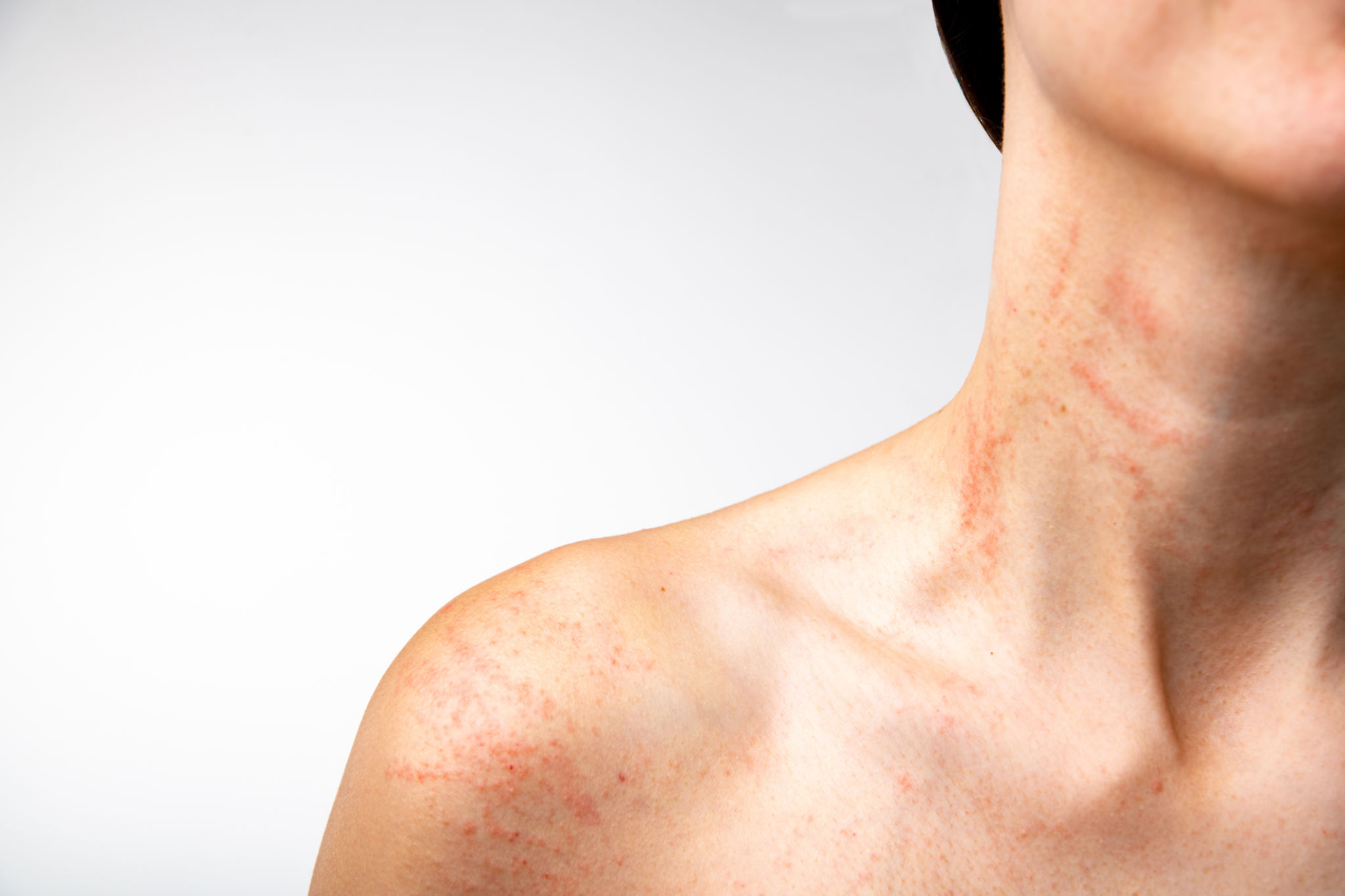
What are the Causes
- Allergies– for example:
- Food allergies such as allergies to nuts, strawberries, citrus fruit, egg, food additives, spices, chocolate, or shellfish. Sometimes you can develop an allergy to a food even if you have eaten it without any problem many times before.
- Allergies to insect bites and stings.
- Allergies to medicines such as penicillin, aspirin, anti-inflammatory painkillers, etc.
- A viral infectionsuch as a cold or flu can trigger an urticarial rash in some people. (You react to the virus.) A mild viral infection which causes few other symptoms is probably a common trigger of an urticarial rash that develops without an apparent cause.
- Skin contactwith sensitisers causes a local area of urticaria in some people. For example, chemicals, latex, cosmetics, plants, ointments, nettle stings, etc.
- Physical urticaria. This is a type of urticaria in which a rash appears when the skin is physically stimulated. The most common is called dermatographism (dermatographia) when a rash develops over areas of skin which are firmly stroked. Sometimes an urticarial rash is caused by heat, cold, emotion, exercise, or strong sunlight.
Treatment
- A cool bath or shower may ease the itch.
- Calamine lotion or menthol 1% in aqueous cream can help with itching.
- Antihistamine tablets can ease symptoms.
- If you can identify a trigger such as a food, then it would be sensible to avoid it in the future.
- A short course of steroid tablets is sometimes prescribed in severe cases to help reduce swelling in the skin.
- If extra control is needed you may be prescribed an antileukotriene medicine. These medicines also help to block the action of histamine and are intended to be taken with antihistamines.